In many Nigerian homes, urinary problems are rarely discussed openly. Frequent urination at night, weak urine stream, burning sensation, or lower abdominal discomfort are often accepted as part of aging or managed quietly with herbal mixtures and over-the-counter drugs. For many men in particular, symptoms are ignored for years until they begin to disrupt sleep, work, and daily life.
Yet chronic urinary tract and prostate disorders in Nigeria are common and increasingly affect quality of life for adults, especially middle-aged and older men. These conditions often develop slowly, making them easy to overlook in the early stages. Recurrent urinary tract infections, enlarged prostate, chronic prostatitis, and bladder problems can all progress silently, leading to complications when care is delayed.
From everyday clinical experience, late presentation, embarrassment, misinformation, and reliance on self-medication are major reasons these disorders worsen. When identified early and managed properly, many urinary and prostate conditions can be controlled effectively, reducing discomfort and preventing long-term damage.
This article explains chronic urinary tract and prostate disorders in Nigeria in clear, practical terms—covering common conditions, causes, symptoms, health risks, diagnosis, treatment options, and realistic steps for long-term management and prevention—so individuals can seek care early and protect their health with confidence.
Understanding Chronic Urinary Tract and Prostate Disorders
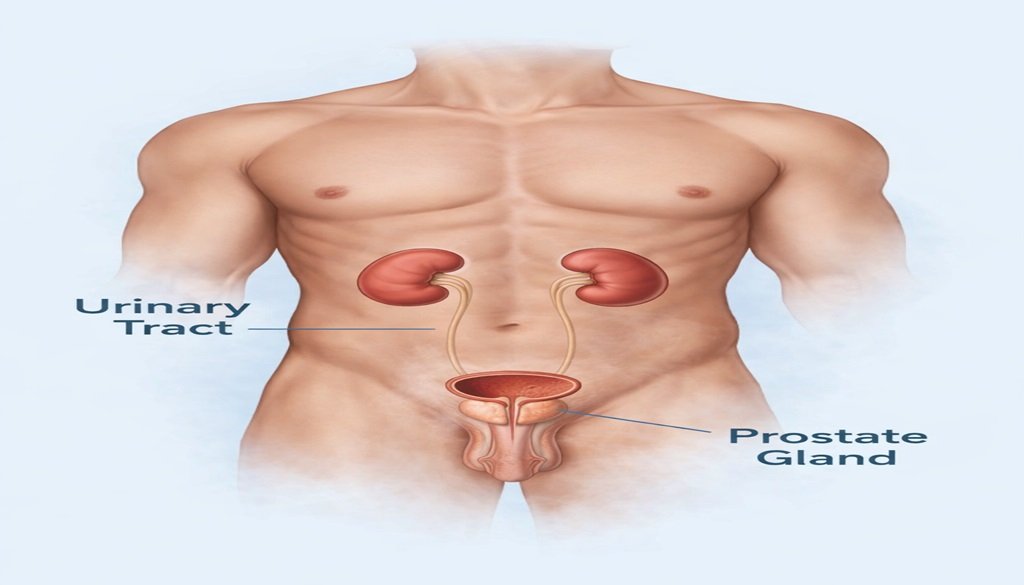
The urinary tract consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Its main function is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body through urine. In men, the prostate gland sits just below the bladder and surrounds part of the urethra. The prostate plays a role in producing seminal fluid, but because of its position, any enlargement or inflammation can directly affect urination.
Urinary tract and prostate disorders can be acute or chronic. Acute conditions develop suddenly and may resolve with treatment, while chronic disorders persist for months or years, often with recurring symptoms. Chronic conditions usually require long-term management rather than one-time treatment.
In Nigeria, chronic urinary and prostate disorders are common but underdiagnosed. Many people delay seeking care until symptoms become severe or complications develop.
Common Chronic Urinary Tract Disorders in Nigeria
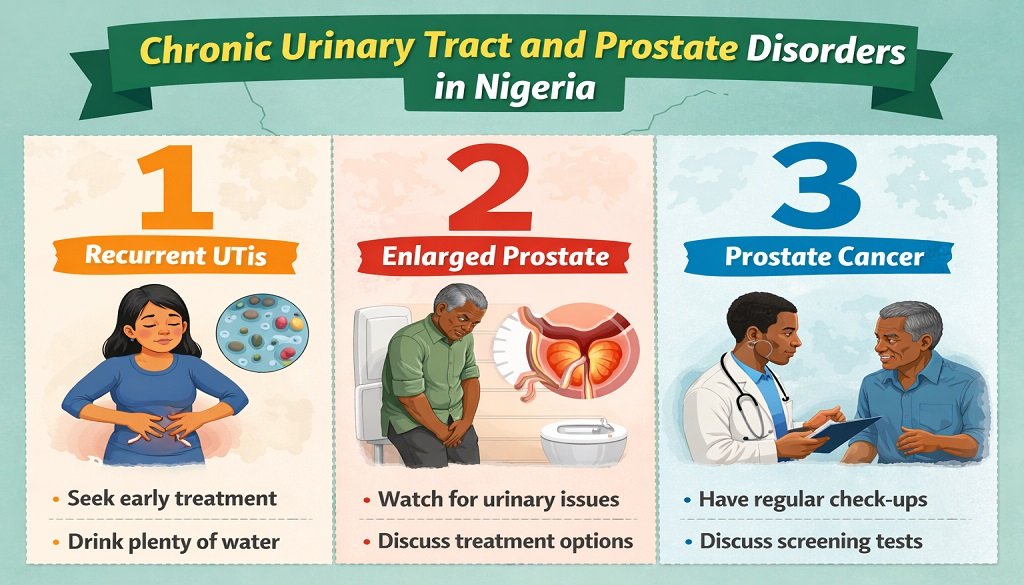
Several long-term urinary tract conditions affect Nigerians across different age groups.
Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply. When infections occur repeatedly or fail to clear completely, they are described as recurrent or chronic UTIs.
Common symptoms include:
- Burning or pain during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Passing small amounts of urine
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Lower abdominal discomfort
Recurrent UTIs may result from incomplete treatment, poor hygiene, underlying urinary obstruction, diabetes, or prostate enlargement in men. Repeated infections can damage the urinary tract and kidneys if not properly managed.
Chronic Cystitis
Chronic cystitis refers to long-term inflammation of the bladder. It may develop after repeated infections or from non-infectious causes such as irritation, bladder dysfunction, or underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms often include persistent bladder discomfort, frequent urination, urgency, and pelvic pain. Because symptoms can resemble those of simple UTIs, proper diagnosis is essential.
Urinary Retention and Flow Problems
Urinary retention occurs when the bladder does not empty completely. This condition is often linked to prostate enlargement but may also result from nerve damage, infections, or certain medications.
Symptoms include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream
- Dribbling after urination
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
Chronic retention increases the risk of infections, bladder damage, and kidney complications.
Common Prostate Disorders in Nigeria
Prostate disorders become more common with increasing age, but younger men can also be affected.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It is one of the most common prostate disorders among Nigerian men over the age of 50.
As the prostate enlarges, it compresses the urethra and interferes with urine flow. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Straining during urination
Although BPH is not cancer, untreated symptoms can lead to serious complications such as urinary retention and kidney damage.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland and may be caused by bacterial infection or non-infectious factors. It can occur in younger and older men.
Symptoms may include:
- Pelvic or lower back pain
- Painful urination or ejaculation
- Frequent urination
- Fever in acute cases
Chronic prostatitis can be difficult to diagnose and treat, often requiring long-term management.
Prostate Cancer (Brief Overview)
Prostate cancer is distinct from benign prostate disorders but may present with similar urinary symptoms in its early stages. Early prostate cancer may cause no symptoms at all.
Routine screening and medical evaluation help differentiate cancer from non-cancerous conditions and improve outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors in Nigeria
Chronic urinary tract and prostate disorders arise from a combination of biological, lifestyle, and healthcare-related factors.
Infections and Inflammation
Untreated or poorly treated urinary infections contribute to chronic inflammation of the bladder and prostate. Poor access to healthcare and delayed diagnosis increase the likelihood of complications.
Aging and Hormonal Changes
Age-related hormonal changes cause gradual prostate enlargement in many men. This natural process explains why prostate disorders are more common in older age groups.
Lifestyle and Health Factors

Physical inactivity, obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of urinary and prostate problems. Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes also raise susceptibility to infections and urinary complications.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Persistent urinary or prostate symptoms should never be ignored. Warning signs include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Pain or burning during urination
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Difficulty starting urination
- Blood in urine or semen
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
Symptoms that worsen over time or interfere with daily life require medical evaluation.
Health Risks and Complications
Untreated urinary and prostate disorders can lead to serious health consequences.
Kidney Damage and Recurrent Infections
Backflow of urine due to obstruction increases pressure on the kidneys, leading to kidney damage. Recurrent infections further worsen kidney function over time.
Bladder Damage and Stones
Chronic urinary retention stretches and weakens the bladder. This may lead to bladder stones, infections, and loss of bladder control.
Impact on Quality of Life
Frequent urination disrupts sleep and daily activities. Chronic discomfort affects emotional wellbeing, sexual health, and social interactions, leading to stress and reduced quality of life.
How Urinary Tract and Prostate Disorders Are Diagnosed
Diagnosis begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Doctors may perform specific tests to identify the underlying cause.
Common diagnostic methods include:
- Urine tests to detect infection or blood
- Blood tests to assess kidney function and prostate markers such as PSA when appropriate
- Ultrasound to evaluate the bladder, kidneys, and prostate
- Specialized urological tests when needed
Accurate diagnosis guides effective treatment and prevents complications.
Living With Chronic Urinary Tract and Prostate Disorders in Nigeria
Although these conditions are long-term, many people achieve good symptom control with appropriate care.
Medical Treatment and Follow-Up
Treatment depends on the specific disorder and may include antibiotics, medications to relax the prostate and bladder muscles, or drugs to reduce prostate size. Regular follow-up ensures treatment remains effective and complications are detected early.
Avoiding self-medication and completing prescribed treatments are essential for long-term success.
The Federal Ministry of Health Nigeria emphasizes early diagnosis and appropriate management of urinary and prostate disorders as part of men’s health care
Lifestyle and Self-Care Measures
Lifestyle changes play an important role in symptom control. These include:
- Maintaining adequate but not excessive fluid intake
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
- Staying physically active
- Avoiding bladder irritants
Healthy habits support urinary function and overall wellbeing.
Monitoring and Long-Term Care

Regular medical reviews, symptom tracking, and early reporting of new symptoms help prevent complications. Long-term care focuses on maintaining comfort, protecting kidney health, and preserving quality of life.
Preventing Chronic Urinary and Prostate Disorders
Preventive measures reduce the risk of long-term urinary problems.
Effective strategies include:
- Good personal hygiene
- Early treatment of urinary infections
- Healthy diet and regular exercise
- Limiting alcohol and avoiding smoking
- Routine screening for at-risk age groups
Public awareness and early intervention significantly improve outcomes.
When to See a Doctor for Urinary or Prostate Symptoms
Medical care should be sought if urinary symptoms persist, worsen, or include warning signs such as blood in urine, severe pain, fever, or sudden inability to pass urine. Early evaluation prevents complications and improves treatment success.
Common Myths About Urinary and Prostate Disorders in Nigeria
Misinformation often delays care and worsens disease outcomes.
- Urinary problems are normal with age.
While some changes occur with aging, persistent symptoms are not normal and should be evaluated. - Prostate problems always mean cancer.
Most prostate disorders are non-cancerous and manageable. - Herbal remedies can permanently cure prostate disorders.
There is no scientific evidence that herbal treatments cure chronic prostate conditions.
Replacing myths with accurate information encourages timely and appropriate care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are chronic urinary tract and prostate disorders?
They are long-term conditions affecting the urinary system or prostate that cause persistent or recurring symptoms.
Are prostate disorders common in Nigerian men?
Yes. Prostate disorders, especially BPH, are common and increase with age.
Can chronic UTIs be cured?
Recurrent UTIs can often be controlled and prevented with proper diagnosis and treatment.
Does frequent urination always mean prostate disease?
No. Other conditions such as infections, diabetes, or bladder disorders may cause similar symptoms.
When should urinary symptoms be treated urgently?
Severe pain, blood in urine, fever, or inability to pass urine require urgent medical attention.
Final Thoughts
Chronic urinary tract and prostate disorders in Nigeria are common but manageable conditions. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and consistent follow-up significantly reduce complications and improve quality of life.
Ignoring symptoms or relying on self-medication increases the risk of long-term damage. Seeking timely medical care and adopting healthy lifestyle habits remain the most effective ways to protect urinary and prostate health.
This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical guidance.